- a computing technique that enables quick retrieval of frequently accessed data
- When a client/server request is made without caching, the client sends a request to the service, which then retrieves data from storage and sends it back to the client.
- retrieving data from storage can become slow and overloaded with high volumes of traffic
- Adding a cache to the system can help overcome these limitations. When data is requested, the service first checks the cache for the data. If the data is present in the cache, it is quickly returned to the service
- If the data is not found in the cache, the service retrieves it from storage, stores it in the cache, and then responds to the client.
Cache systems vs storage systems
-
cache systems store frequently accessed data in memory. Storage systems store data on disks.
-
memory is more expensive than disk, so cache systems typically have much smaller data capacity than storage systems
-
the data stored in cache systems are not designed for long-term data persistence and durability. In contrast, storage systems are designed to provide long-term data persistence and durability, ensuring that data is always available when needed.
-
cache systems are optimized for supporting heavy traffic and high concurrency. Storage systems, are better suited for durably storing and managing large amounts of data.
-
cache hit vs cache miss
-
cache hit ratio (cache effectiveness)
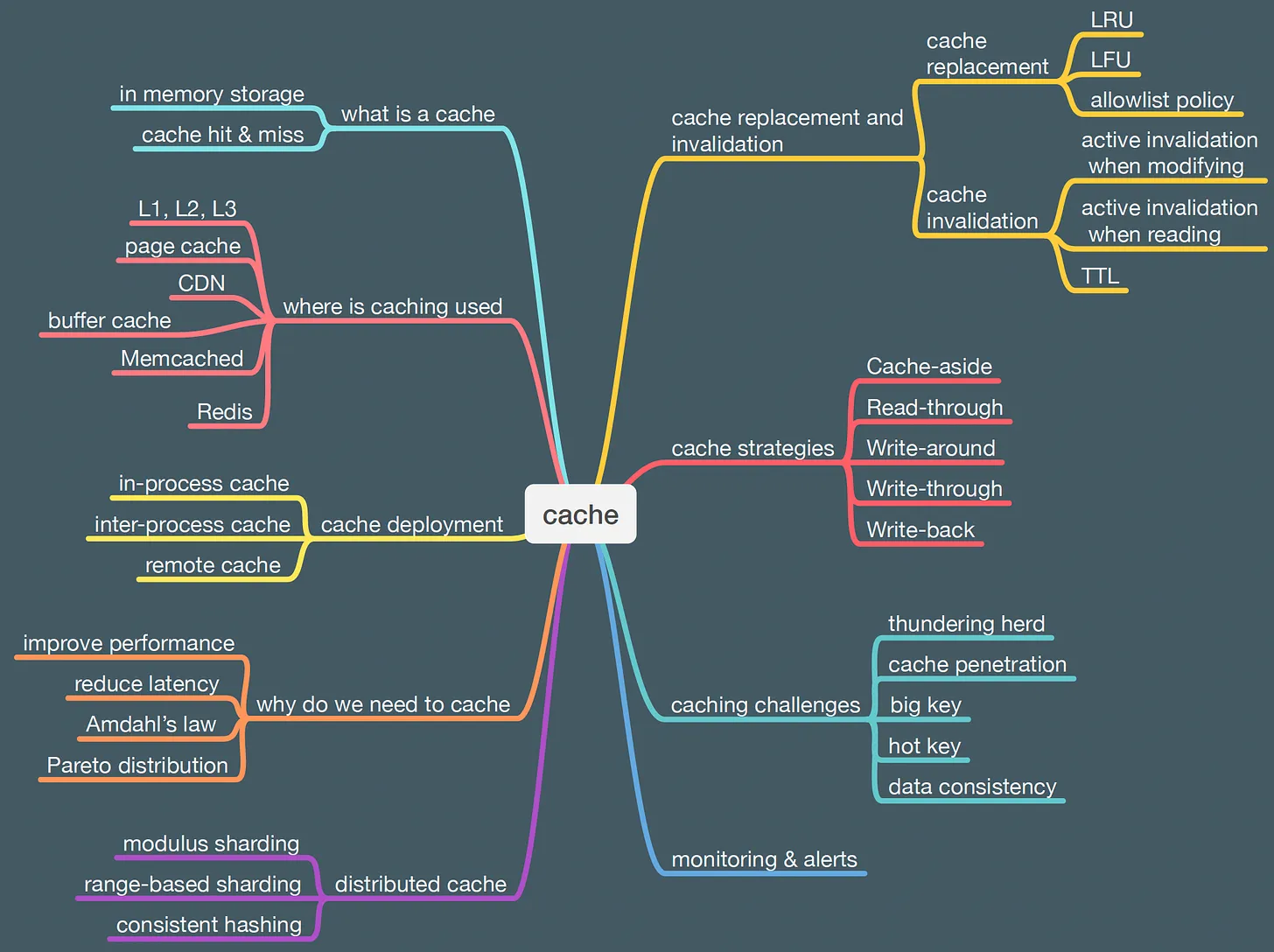
Where is caching used
- Modern computers utilize multiple levels of cache, including the L1, L2, and L3 caches, to provide fast access to frequently used data for the CPU.
- The Memory Management Unit (MMU) is responsible for mapping virtual memory addresses to physical memory addresses.
- The MMU contains a specialized cache called the Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB), which stores the most recently used address translations to speed up the address translation process.
- Two widely used caching systems are Memcached and Redis. They are open-source, high-performance, distributed caching systems that can be used to store and retrieve data quickly.
In conclusion
Caching is an effective solution for scenarios where data changes infrequently, the same data is accessed multiple times, the same output is produced repeatedly, or the results of time-consuming queries or calculations are worth caching.