⬅️Architecture 🔗 YT
1. Layered Architecture
- separate the components of a system into distinct layers (presentation layer, business layer, persistence layer, database layer…)
- MVP is an example of that too
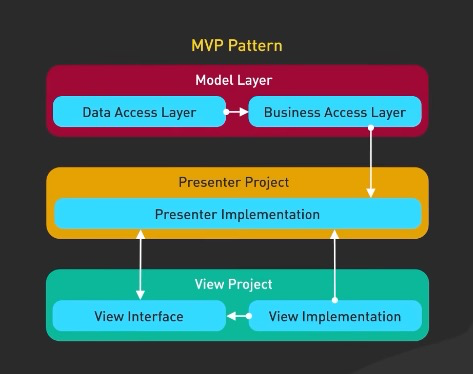
- promotes separation of concerns (so changes in one layer don’t affect another layer)
- provides abstraction and encapsulation
2. Event-Driven Architecture
- loosely coupled software components and services
- components broadcast events when something happens, other components subscribe to the events they are interested in (pub-sub model)
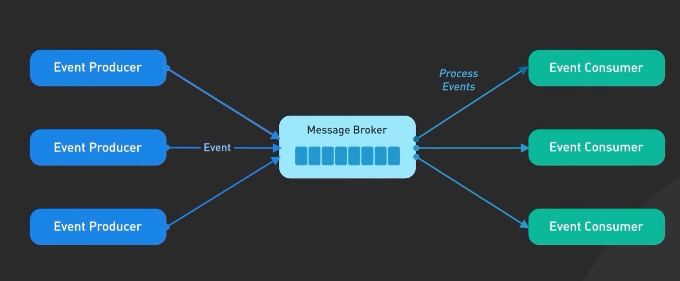
- highly decoupled
- example:
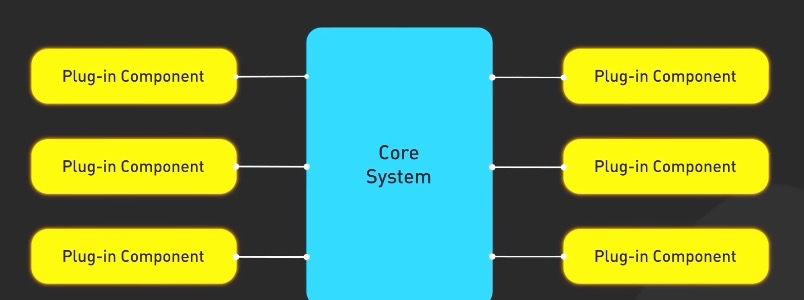
3. Micro-Kernel Architecture
- separates core system functionalities, into small micro kernels (add-ons, plugins)
- e.g. OS components
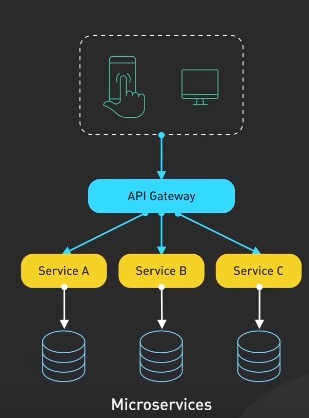
4. Microservices Architecture
- the application is broken down into a collection of small, loosely coupled services
- e.g. Netflix
- services can be developed, deployed and scaled independently
- tradeoff: added complexity in intra-service communication and maintaining data consistency
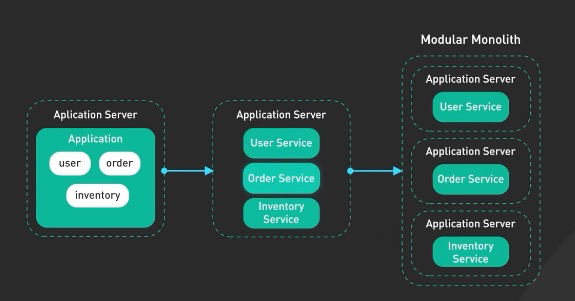
5. Monolithic Architecture
- simplifies development and deployment (go-to for startups and smaller applications)
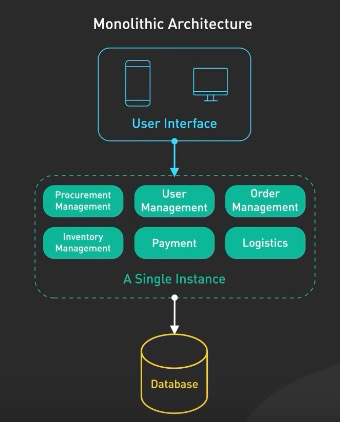
- on the rise is the modular monolith
- still single deployable unit but with modular boundaries