- from construction point of view
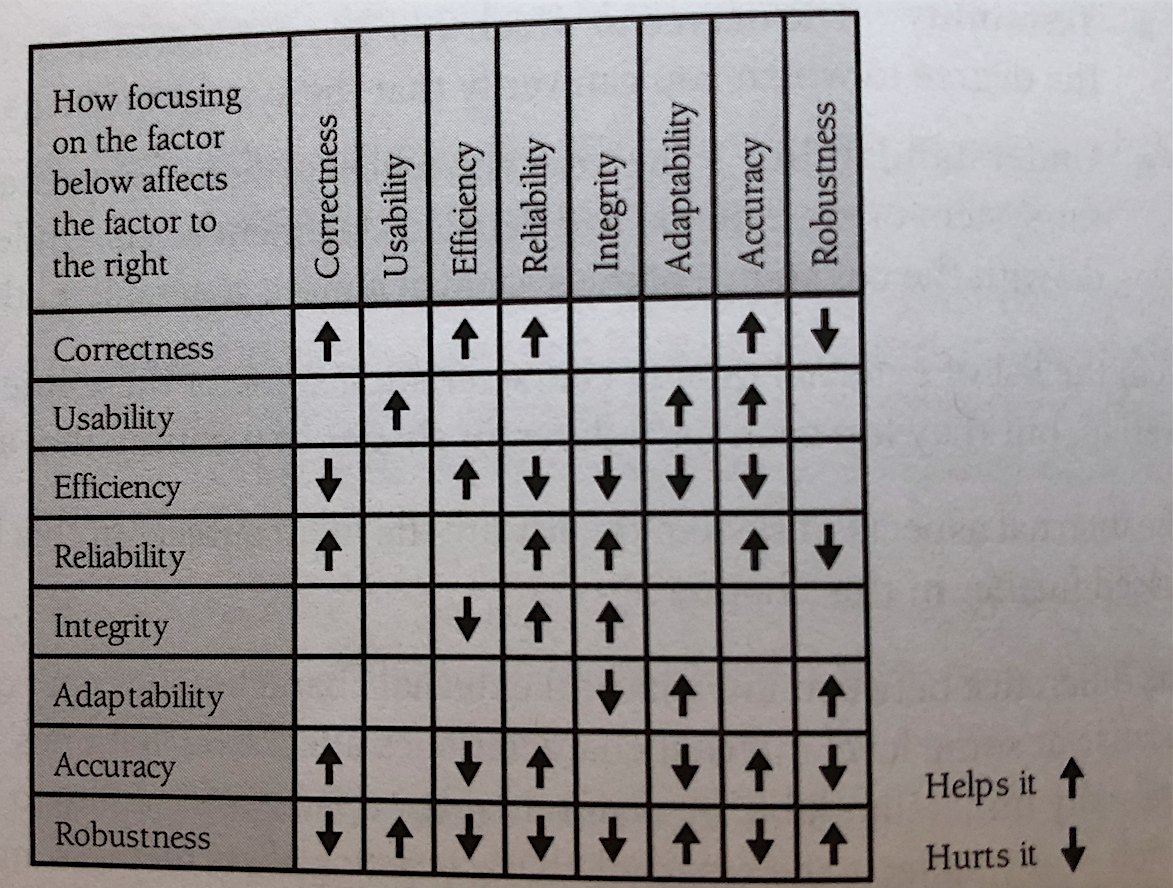
Characteristics of software quality:
External (users care about this):
- correctness
- usability
- efficiency
- reliability
- integrity (restricting non-auth users)
- adaptability
- accuracy
- robustness (continued function even under unanticipated conditions)
Internal:
- maintanability
- flexibility
- portability
- reusability
- readability
- testability
- understandability
Finding an optimal solution from a set of competing objectives is one activity that makes software development a true engineering discipline.
Techniques for improving software quality
-
software-quality objectives: setting explicit goals, mixing internal/external characteristics
-
explicit quality-assurance activity: the organization must show programmers that quality is a priority
-
testing strategy
-
software engineering guidelines
-
informal and formal technical reviews
-
external audits
-
avoid uncontrolled changes
-
prototyping
-
Regarding setting objectives: The surprising implication is that people actually do what you ask them to do.
-
Different people tend to find different defects, and it’s best to do a combination of defect-detecting efforts.
-
A study found that code reading detected about 80% more faults per hour than testing
Recommended combination for achieving higher-than-average quality:
- formal inspections of all requirements, all architecture, and designs for critical parts of a system
- modeling or prototyping
- code reading or inspections
- execution testing
You should emphasize quality-assurance work in the early stages and throughout the rest of the project.
- General principles of Software quality: improving quality reduces development costs
- the best way to improve productivity and quality is to reduce the time spent reworking code
- The industry average: 10-50 lines of code delivered per person/per day
- The single biggest activity on most projects is debugging and correcting code that doesn’t work properly